BGP For Boneheads
 Today we’ll go over a quick BGP lab environment using four virtual Cisco CSR1000V routers (IOS-XE based) and a pair of Linux end hosts. I’ll try to explain the configuration as best I can but you should know that I have no idea what I’m doing. This lab is the result of numerous Google searches and a beer or two. Or six.
Today we’ll go over a quick BGP lab environment using four virtual Cisco CSR1000V routers (IOS-XE based) and a pair of Linux end hosts. I’ll try to explain the configuration as best I can but you should know that I have no idea what I’m doing. This lab is the result of numerous Google searches and a beer or two. Or six.
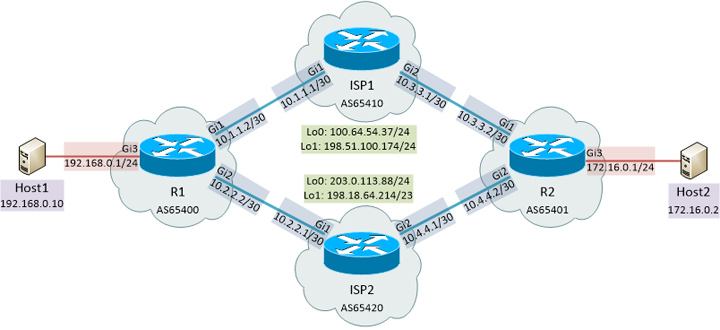
Above is the topology for my lab environment. I wanted to simulate two end clients both peering to a pair of ISPs. I used /24’s for the “inside” network for each client and /30’s for BGP connectivity. I also threw some loopback addresses on the ISP routers based on RFC 6598/2544/5737 reserved blocks so the routing table wouldn’t be empty.
With the previously seen topology, here is what a trace looks like between the two end hosts:
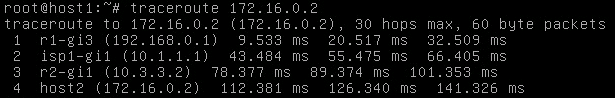
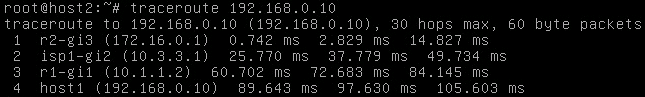
Both directions are passing through the ISP1 router. What I did next is a hard BGP reset on ISP1 using clear ip bgp * so the sessions would briefly drop. Our path between the two end hosts now goes over ISP2:
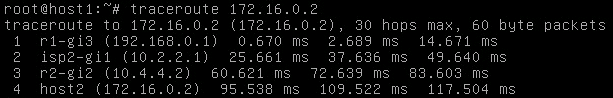
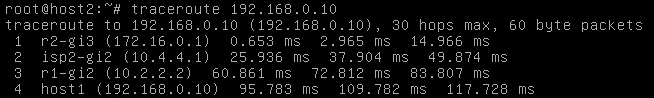
Now I’ll dump the configs of the four routers and explain why I used what I did.
! R1 router bgp 65400 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp dampening network 192.168.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0 neighbor ISP1 peer-group neighbor ISP1 remote-as 65410 neighbor ISP1 version 4 neighbor ISP1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor ISP1 prefix-list OUTBOUND out neighbor ISP2 peer-group neighbor ISP2 remote-as 65420 neighbor ISP2 version 4 neighbor ISP2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor ISP2 prefix-list OUTBOUND out neighbor 10.1.1.1 peer-group ISP1 neighbor 10.2.2.1 peer-group ISP2 ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0 ip prefix-list OUTBOUND seq 5 permit 192.168.0.0/16 le 32 ! R2 router bgp 65401 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp dampening network 172.16.0.0 mask 255.255.255.0 network 172.16.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0 neighbor ISP1 peer-group neighbor ISP1 remote-as 65410 neighbor ISP1 version 4 neighbor ISP1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor ISP1 prefix-list OUTBOUND out neighbor ISP2 peer-group neighbor ISP2 remote-as 65420 neighbor ISP2 version 4 neighbor ISP2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor ISP2 prefix-list OUTBOUND out neighbor 10.3.3.1 peer-group ISP1 neighbor 10.4.4.1 peer-group ISP2 ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.255.0 Null0 ip route 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 Null0 ip prefix-list OUTBOUND seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/24 le 32 ip prefix-list OUTBOUND seq 10 permit 172.16.1.0/24 le 32 ! ISP1 router bgp 65410 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp dampening redistribute connected neighbor R1 peer-group neighbor R1 remote-as 65400 neighbor R1 version 4 neighbor R1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor R1 prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT in neighbor R2 peer-group neighbor R2 remote-as 65401 neighbor R2 version 4 neighbor R2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor R2 prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 in neighbor 10.1.1.2 peer-group R1 neighbor 10.3.3.2 peer-group R2 distribute-list prefix NOPE out ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT seq 5 permit 192.168.0.0/16 le 32 ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/24 le 32 ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 seq 10 permit 172.16.1.0/24 le 32 ip prefix-list NOPE seq 5 deny 10.0.0.0/8 le 32 ip prefix-list NOPE seq 20 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 ! ISP2 router bgp 65420 bgp log-neighbor-changes bgp dampening redistribute connected neighbor R1 peer-group neighbor R1 remote-as 65400 neighbor R1 version 4 neighbor R1 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor R1 prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT in neighbor R2 peer-group neighbor R2 remote-as 65401 neighbor R2 version 4 neighbor R2 soft-reconfiguration inbound neighbor R2 prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 in neighbor 10.2.2.2 peer-group R1 neighbor 10.4.4.2 peer-group R2 distribute-list prefix NOPE out ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT seq 5 permit 192.168.0.0/16 le 32 ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 seq 5 permit 172.16.0.0/24 le 32 ip prefix-list IN-FROM-CLIENT2 seq 10 permit 172.16.1.0/24 le 32 ip prefix-list NOPE seq 5 deny 10.0.0.0/8 le 32 ip prefix-list NOPE seq 20 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32
On R1 I advertised the prefix 192.168.0.0/16 though as you saw in the topology we only actually used a /24. On R2 I advertised two /24s with one going to the end host and another actually attached to a loopback interface. For the neighbor configuration on all routers I used peer groups to make it a little easier to read. I also used prefix-list for the outbound routes on the client routers and for the inbound routes on the ISP routers. On the ISP routers I set it to redistribute connected interfaces so I could get the loopback subnets in the routing table, but this also redistributed the /30 links to both client routers. To get around this I created the NOPE prefix-list denying 10.0.0.0/8 and used distribute-list prefix NOPE out on each ISP router. Below you can see the BGP routes on each client router:
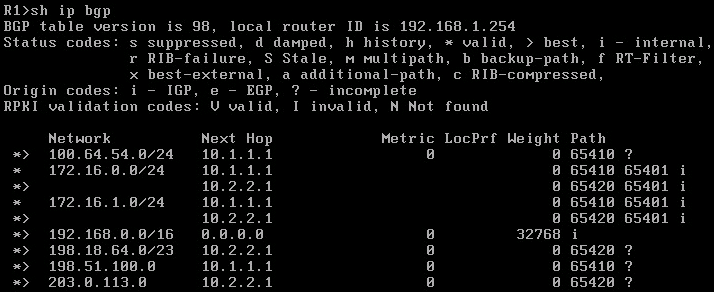
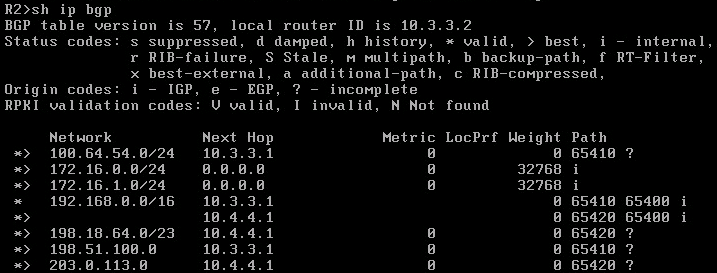
So there you have it. Possibly at some point in the future I’ll revisit this with route maps, community strings, neighbor weight and influencing routing paths but as previously stated I have no idea what I’m doing. This was simply an experiment to see if I could…